联系方式
more本类最新英语论文
- 2017-10-06中国能源政策的有用特征:‘..
- 2017-08-20新型二维材料石墨graphene:..
- 2016-08-09机械工程系本科essay:世界..
- 2016-04-14光电效应photoelectric eff..
- 2016-02-03起源、历史和保护玻璃
- 2015-10-08science technology:成像触..
- 2015-08-29技术发展对社会的影响
- 2015-06-02文化和科技进步
- 2015-03-27脸部识别技术及运用
- 2015-02-11脸部识别方法简介的英国留学..
more热门文章
- 2010-11-21对水产养殖品的营养物质研究
- 2011-01-26英国赫尔大学留学生毕业论文..
- 2009-04-18保护环境论文
- 2010-10-06a practitioner’s view of..
- 2010-10-01solar radiation predictio..
- 2010-05-22a decision matrix for cho..
- 2010-04-05self-diffusion of colloid..
- 2007-08-06a high resolution finite ..
- 2016-02-03起源、历史和保护玻璃
- 2012-08-18美国electrical engineerin..
more留学论文写作指导
- 2024-03-31卡森•麦卡勒斯小说中..
- 2024-03-28美国黑人女性心理创伤思考—..
- 2024-03-27乔治·艾略特《织工马南》中..
- 2024-03-21超越凝视:论《看不见的人》..
- 2024-03-19《哈克贝利•费恩历险..
- 2024-03-13心灵救赎之旅——从凯利的三..
- 2024-02-22文学地理学视角下的《印度之..
- 2023-05-03英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰..
- 2023-02-07目的论视域下5g—the futur..
- 2022-07-04二语英语和三语日语学习者的..
新型二维材料石墨Graphene: Novel Two-dimensional Material [2]
论文作者:www.51lunwen.org论文属性:学术文章 Scholarship Essay登出时间:2017-08-20编辑:anne点击率:7700
论文字数:1157论文编号:org201708201544121229语种:英语 English地区:英国价格:免费论文
关键词:新型二维材料石墨GrapheneNovel Two-dimensional Material
摘要:本文是对石墨烯的一个很好的介绍,并在各个领域的运用和开发,总结了在这方面所做的工作。
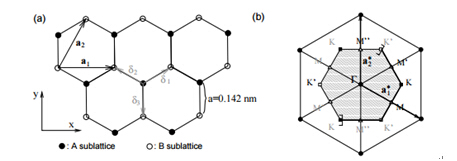
Figure 2. (a) Honeycomb lattice of graphene; (b) Reciprocal lattice of the triangular lattice.
2.2 Electrical properties
Graphene exhibits excellent electrical conductivity(ballistic transport of electron carriers) with an intrinsic mobility of 200,000 cm2/V∙s in extreme cases and 15,000 cm2/V∙sunder ambient conditions, which are several orders of magnitude higher than that of copper, the most commonly used conductor nowadays. It is a zero-gap semiconductorwhose conduction and valence bands meet at the Dirac points (see Figure 3).The uniquehoneycomb lattice structure leads to the fact that the first Brillouinzone possesses two points on the edge that are non-equivalent to each other (K/K’points, which areknown as Dirac points). Thetight-bindingapproach focused on the nearest neighbour interactionprovides the dispersion relation of the electrons near the K/K’points:
 (1)
(1)where α= √3 a_cc, acc is the length of C-C bond (0.142 nm), γ0 is the nearest-neighbor hopping energywith a magnitude of 2.8 eV. The positive sign applies to empty conduction (π) bands, while the negative sign corresponds to fully occupied valence (π*) bands.
The dispersion near the K/K’points can be obtained by:
 (2)
(2)whereq ⃗is the momentum corresponding to the Dirac point, h ̅=h/2π and h is Planck’s constant. V_F=√3 ta/2 is the Fermi velocity and the value is 1×106 m/s.
Theelectrons’ linear dispersion relation can be described by:
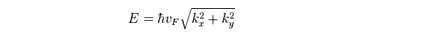 (3)
(3)where k is a wave-vector measured from the Dirac points.
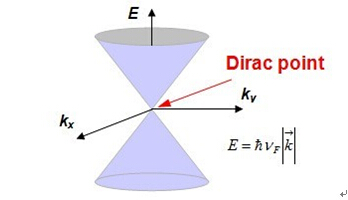
Figure 3. Electronic structure of graphene.
2.3 Mechanical properties
Previous studies claimed that graphene is the strongest natural material that has ever been discovered. The intrinsic tensile strength and Young's modulus of defect free graphene are 130 GPa and 1 TPa, respectively(Lee et al., 2008), indicating outstanding mechanical strength. Meanwhile, the flexibility of graphene is (elastic modulus = 32 GPa)also reasonably high and can be further improved by introducing chemical cross-linking between individual layers. Additionally, the stiffness of graphene is 0.5 TPa and this material exhibits brittle fractures(as in cases of ceramic materials)(Zhang et al., 2014). Therefore, graphene may be used as pressure sensors.
2.4Magnetic properties
Previous
Potential applications
Current and future applications will be summarized to show the great potential of graphene in industrial applications.
Conclusions and perspectives

 英国
英国 澳大利亚
澳大利亚 美国
美国 加拿大
加拿大 新西兰
新西兰 新加坡
新加坡 香港
香港 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 法国
法国 德国
德国 爱尔兰
爱尔兰 瑞士
瑞士 荷兰
荷兰 俄罗斯
俄罗斯 西班牙
西班牙 马来西亚
马来西亚 南非
南非






