联系方式
more本类最新英语论文
- 2024-05-14《反论》(节选)英汉翻译实..
- 2024-05-07《湖泊的一生》(节选)英汉..
- 2024-03-31卡森•麦卡勒斯小说中..
- 2024-03-28美国黑人女性心理创伤思考—..
- 2024-03-27乔治·艾略特《织工马南》中..
- 2024-03-21超越凝视:论《看不见的人》..
- 2024-03-19《哈克贝利•费恩历险..
- 2024-03-13心灵救赎之旅——从凯利的三..
- 2024-02-22文学地理学视角下的《印度之..
- 2023-05-03英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰..
more热门文章
- 2009-03-31the comparison of family ..
- 2010-04-02英语毕业论文范文 委婉语的..
- 2011-03-17代写英语毕业论文:global ..
- 2009-04-16常用经典英语论文写作句型
- 2009-04-17apa格式 英语论文中的apa格..
- 2015-05-13英语毕业论文范文:marketin..
- 2010-07-26英语毕业论文指导
- 2009-04-21原创优秀英语教学毕业论文范..
- 2010-09-18英语跨文化交际教学硕士毕业..
- 2010-12-26“迷惘”的主题之评析《永别..
more留学论文写作指导
- 2024-05-14《反论》(节选)英汉翻译实..
- 2024-05-07《湖泊的一生》(节选)英汉..
- 2024-03-31卡森•麦卡勒斯小说中..
- 2024-03-28美国黑人女性心理创伤思考—..
- 2024-03-27乔治·艾略特《织工马南》中..
- 2024-03-21超越凝视:论《看不见的人》..
- 2024-03-19《哈克贝利•费恩历险..
- 2024-03-13心灵救赎之旅——从凯利的三..
- 2024-02-22文学地理学视角下的《印度之..
- 2023-05-03英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰..
英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰语移位对比探讨
论文作者:留学生论文论文属性:硕士毕业论文 dissertation登出时间:2023-05-03编辑:vicky点击率:2657
论文字数:论文编号:org202304272131022900语种:英语 English地区:中国价格:$ 44
关键词:英语毕业论文范文
摘要:本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本文缺乏对双音节形容词在主名短语中表达情感或情绪到状语位置的运动动机的研究。此外,经历特殊形态变化的形容词所包含的强焦点特征还需要进一步证明,以证明这一观点的有效性。此外,语言学界对阶段的定义还不太清楚,迄今为止也没有达成一致意见。
本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本文讨论了英汉形容词在名词短语中的运动,在阶段理论和制图方法的框架下探讨了形容词的运动机制,并从形式句法的角度解释了形容词运动的派生过程。
Chapter One Introduction
1.1 Research Background
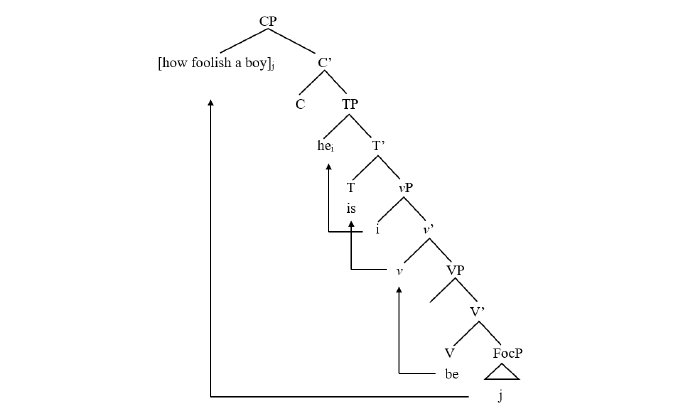
Adjective is a kind of word categories, which modifies a noun and indicates the nature, state, feature or attribute of a person or thing. Many languages contain adjectives in the division of word of speech and English and Chinese are no exception. However, due to uniqueness of languages, even the same word of speech may have respective syntactic functions and lexical meanings in different languages. In English, adjectives generally serve as attributive, predicative and complement. In Chinese, because Chinese lacks of strict morphological standards, adjectives can exist almost anywhere in the sentence, that is, they can act as subject, predicate, object, attributive, adverbial and complement to modify different grammatical components. It can be known that functioning as attributive is the main syntactic function of adjectives in English and Chinese. Generally speaking, adjectives are placed after articles and before nouns in nominal phrases, which forms structural sequence “Art+Adj+N”, such as “一座高的楼” in Chinese or “a good boy” in English. However, adjectives can appear before articles like “很高的一座楼” or “so good a boy” due to some reasons in English and Chinese. What’s more, adjectives in Chinese can even appear in adverbial position, while their meanings still point to nominal elements like the adjective “高高地” still modifies noun “楼” in “他高高地盖了一座楼”. However, there is no such phenomena in English for that “*He so tall built a building” is illegal. How to explain this difference is the problem that needs to be explored in this paper.
1.2 Research Objective
According to observed linguistic facts, it is phenomenon that adjectives change their original position in sentences that should be treated as research objectives. However, although in some conditions adjectives do appear in different positions, they don’t belong to research scope of this thesis. Consider the following examples:
(1) a. so clever a boy
b. how difficult a clue (it is) c. 很高的/高高的一座楼 d. 他高高地盖了一座楼。 e. 他冷冷地看了我一眼。
(2) a. more/less complicated a pattern (than) a’. *a more/less complicated pattern (than) a’’. a pattern more/less complicated (than) b. far/even/any/much/no bigger a threat (than) b’. *a far/even/any/much/no bigger threat (than) b’’. a threat far/even/any much/no bigger (than) c. as good a place (as) c’. *a as good place (as) c’’. a place as good (as) d. a cause strange enough (to) e. 他慢慢地站起身来。 f. 他黑黑地染了发。 g. 领导逼他老老实实地写材料。
In examples 1a-1b, English adjectives can change from attributive position into position before articles. In 1a, when “clever” co-occurs with degree word “so”, they undergo leftward movement together, resulting in different position of adjective in nominal phrase. In 1b, when “different” combines with “how”, they also move to position before articles, the difference lies in that not only the adjective moves to left side of nominal phrases but also the whole nominal phrase moves to beginning to form an exclamatory sentence. In 1c-1e, Chinese adjectives can change from attributive position into other positions according to dif本论文由英语论文网提供整理,提供论文代写,英语论文代写,代写论文,代写英语论文,代写留学生论文,代写英文论文,留学生论文代写相关核心关键词搜索。

 英国
英国 澳大利亚
澳大利亚 美国
美国 加拿大
加拿大 新西兰
新西兰 新加坡
新加坡 香港
香港 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 法国
法国 德国
德国 爱尔兰
爱尔兰 瑞士
瑞士 荷兰
荷兰 俄罗斯
俄罗斯 西班牙
西班牙 马来西亚
马来西亚 南非
南非






