联系方式
more本类最新英语论文
- 2024-03-31卡森•麦卡勒斯小说中..
- 2024-03-28美国黑人女性心理创伤思考—..
- 2024-03-27乔治·艾略特《织工马南》中..
- 2024-03-21超越凝视:论《看不见的人》..
- 2024-03-19《哈克贝利•费恩历险..
- 2024-03-13心灵救赎之旅——从凯利的三..
- 2024-02-22文学地理学视角下的《印度之..
- 2023-05-03英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰..
- 2023-02-07目的论视域下5g—the futur..
- 2022-07-04二语英语和三语日语学习者的..
more热门文章
- 2009-03-31the comparison of family ..
- 2010-04-02英语毕业论文范文 委婉语的..
- 2011-03-17代写英语毕业论文:global ..
- 2009-04-16常用经典英语论文写作句型
- 2009-04-17apa格式 英语论文中的apa格..
- 2015-05-13英语毕业论文范文:marketin..
- 2010-07-26英语毕业论文指导
- 2009-04-21原创优秀英语教学毕业论文范..
- 2010-09-18英语跨文化交际教学硕士毕业..
- 2010-12-26“迷惘”的主题之评析《永别..
more留学论文写作指导
- 2024-03-31卡森•麦卡勒斯小说中..
- 2024-03-28美国黑人女性心理创伤思考—..
- 2024-03-27乔治·艾略特《织工马南》中..
- 2024-03-21超越凝视:论《看不见的人》..
- 2024-03-19《哈克贝利•费恩历险..
- 2024-03-13心灵救赎之旅——从凯利的三..
- 2024-02-22文学地理学视角下的《印度之..
- 2023-05-03英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰..
- 2023-02-07目的论视域下5g—the futur..
- 2022-07-04二语英语和三语日语学习者的..
英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰语移位对比探讨 [3]
论文作者:留学生论文论文属性:硕士毕业论文 dissertation登出时间:2023-05-03编辑:vicky点击率:2451
论文字数:论文编号:org202304272131022900语种:英语 English地区:中国价格:$ 44
关键词:英语毕业论文范文
摘要:本文是一篇英语毕业论文,本文缺乏对双音节形容词在主名短语中表达情感或情绪到状语位置的运动动机的研究。此外,经历特殊形态变化的形容词所包含的强焦点特征还需要进一步证明,以证明这一观点的有效性。此外,语言学界对阶段的定义还不太清楚,迄今为止也没有达成一致意见。
3.1 DP Hypothesis .................................... 15
3.2 Phase Theory ................................... 17
Chapter Four Description of Movement of Adjectual Modifiers in English and Chinese Nominal Phrases ...........20
4.1 Classification of English and Chinese Adjectives .......................... 20
4.1.1 Classification of English Adjectives ............................. 20
4.1.1.1 Classification by Grammatical Function ........................ 20
4.1.1.2 Classification by Semantic Meaning ............................. 21
Chapter Five Analysis of Movement of Adjectual Modifiers in English and Chinese Nominal Phrases ...30
5.1 Analysis of Movement of Adjectual Modifiers in English Nominal Phrases ............................. 30
5.1.1 Restrictions on Morphological Change ............................ 30
5.1.2 Restrictions on Semantic Meaning ...................................... 30
Chapter Six Derivation of Movement of Adjectual Modifiers in English and Chinese Nominal Phrases under Phase Theory
6.1 Base-generation Position of Adjectives in Nominal Phrases
Towards status of adjectives, there are mainly three perspectives in academic circles. Abney (1987) analyses adjectives as heads to form maximal projection APs, selecting NPs as complement; Bernstein (1993), Bouchard (1998), et al. argue that adjectives can be analyzed as adjuncts according to adjunction to the maximal projection (NP), the intermediate projection (N’), or the nominal head itself (N); Cinque (1995) believes that adjectives are in specifier positions of FPs in noun phrases by comparing relative position of adjectives in noun phrases in Romance and Germanic languages.
Take nominal phrase “a clever boy” as an example, different syntactic structures are shown in 1a-c.
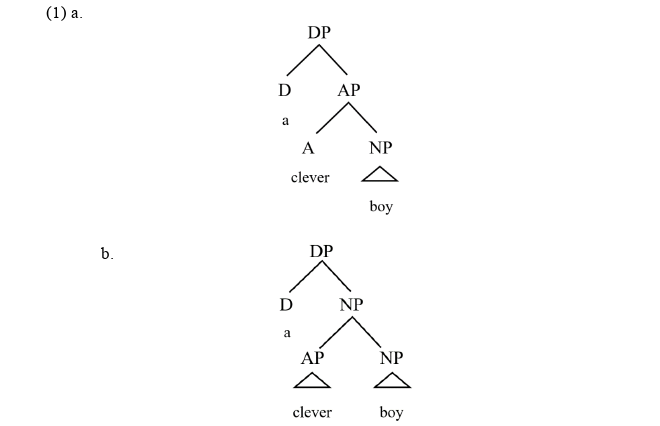
Chapter Seven Conclusion
7.1 Major Findings
This paper discusses movement of English and Chinese adjectives within nominal phrases, explores movement mechanism of adjectives under the framework of Phase Theory and Cartographic Approach and explains derivation process of adjective movement from the perspective of formal syntax. The major findings are as follows:
1) Many English and Chinese adjectual modifiers can undergo movement when meeting several requirements. In semantic level, containment of [+gradable] feature is the premise for adjectives to move, which ensures that they can combine with degree words. What’s more, Chinese adjectives in subject and object nominal phrases have to satisfy extra restrictions to help them enter into adverbial position. Adjectives in object nominal phrases must possess [+perceived] feature while corresponding predicate verbs need to have [+causative] feature to make adjectives salient. Adjectives in subject nominal phrases only need to contain [+temporary] feature for that they undergo movement without going over predicate verbs. In morphological level, English adjectives need to combine with certain degree words to undergo movement, while Chinese adjectives ca本论文由英语论文网提供整理,提供论文代写,英语论文代写,代写论文,代写英语论文,代写留学生论文,代写英文论文,留学生论文代写相关核心关键词搜索。

 英国
英国 澳大利亚
澳大利亚 美国
美国 加拿大
加拿大 新西兰
新西兰 新加坡
新加坡 香港
香港 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 法国
法国 德国
德国 爱尔兰
爱尔兰 瑞士
瑞士 荷兰
荷兰 俄罗斯
俄罗斯 西班牙
西班牙 马来西亚
马来西亚 南非
南非






