联系方式
more本类最新英语论文
- 2023-10-13汉语右移位构式的认知视角探..
- 2022-06-28语境丰富度和二语注释对英语..
- 2021-01-14移动学习模式在高中英语词汇..
- 2017-12-27基于语料库的高中英语词汇教..
- 2017-12-22叙事教学法指导下的高中英语..
- 2017-12-19蒙古族高中生的汉语水平对其..
- 2017-12-17英语词汇触发理论视域下的一..
- 2017-12-13英语专业学生专四写作中的词..
- 2017-12-12基于语料库的中国大学生汉英..
- 2017-11-12中国学习者英语心理词汇的听..
more热门文章
- 2015-06-17英语谚语俗大全(中英对照)
- 2010-02-10neat tricks of vocabulary..
- 2009-04-21英语新词汇的变化和发展
- 2009-12-15不定代词的关联理论和元语用..
- 2009-04-12 2008年英语专业论文题目推..
- 2010-03-01interpersonal meaning of ..
- 2010-02-08探讨词汇习得过程中的特点和..
- 2009-04-04英语新词汇研究
- 2010-06-25vocabulary is a key to en..
- 2009-04-12浅谈英语词汇的发展
more留学论文写作指导
- 2024-03-31卡森•麦卡勒斯小说中..
- 2024-03-28美国黑人女性心理创伤思考—..
- 2024-03-27乔治·艾略特《织工马南》中..
- 2024-03-21超越凝视:论《看不见的人》..
- 2024-03-19《哈克贝利•费恩历险..
- 2024-03-13心灵救赎之旅——从凯利的三..
- 2024-02-22文学地理学视角下的《印度之..
- 2023-05-03英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰..
- 2023-02-07目的论视域下5g—the futur..
- 2022-07-04二语英语和三语日语学习者的..
蒙古族高中生的汉语水平对其英语写作词汇错误的跨语言影响研究 [5]
论文作者:www.51lunwen.org论文属性:硕士毕业论文 thesis登出时间:2017-12-19编辑:lgg点击率:9397
论文字数:38947论文编号:org201712132137144495语种:英语 English地区:中国价格:$ 66
摘要:本文是英语词汇学论文,本研究结果对三语习得理论的发展有所启示,并且对蒙古族地区的外语教学中英语教师的培养、学生英语词汇量的提高、汉语水平的提高及汉语和英语两种语言间的比较对照等方面有所帮助。
Conclusion
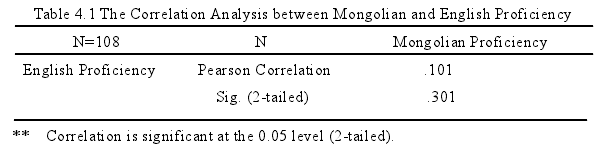
The last chapter is a conclusion part which summarizes major findings for threeresearch questions, discusses theoretical and practical implications, points out somelimitations exist in this study, and puts forward corresponding suggestions for thefurther research.The present study is concerned with the influence of L2 Chinese at the lexicon inMongolian learners’ L3 English writings to confirm L2 interlanguage transferhypothesis through exploring the correlation both between their L1 proficiency andL3 proficiency, and between their L2 proficiency and L3 proficiency, differencesbetween higher L2 proficiency group and lower L2 proficiency group in the lexicaluse, and underlying causes to result in a higher amount of L2 negative transfers incompositions by means of the correlation analysis between scores of L1 Mongolianand L3 English as well as correlation analysis between scores of L2 Chinese and L3English in achievement tests, identification and classification of lexical errors incompositions, and analysis of data collected from questionnaires in order. The majorfindings that have been revealed are listed as follows:
(1) Firstly, as data indicated, there was almost no correlation between L1Mongolian proficiency and L3 English proficiency while there was a low positivecorrelation between L2 Chinese proficiency and L3 English proficiency of Mongolianhigh school students, which indicated that Mongolian learners were much influencedby their L2 Chinese in the production of L3 English lexis rather than L1 Mongolian.
(2) Secondly, our study demonstrated that lexical errors played a vital role inlearners’ errors as a number of errors of lexis were discovered in written essays ofMongolian students. In terms of frequency of ten types of errors in the lexis, errors insubstitution was the most frequently occurred ones, and then errors of absence, wordbuilding, redundancy, spelling, order, part of speech, capitalization, ambiguity andrepetition in order. Generally speaking, it showed that the difference on the frequencyof English lexical errors between higher L2 proficiency group and lower L2 proficiency group was very significant indicating that L2 Chinese played an importantrole in L3 English written productions of two groups of subjects. And both of themmade many lexical errors in L3 English writings, but more lexical errors were foundin students with higher L2 proficiency in comparison with those with lower L2proficiency. Specifically, students who were more proficient in Chinese made moreerrors at the lexical level than those who were less proficient in spelling, wordbuilding, capitalization, order, part of speech, absence and redundancy except forsubstitution, repetition, and ambiguity. Among of them, two kinds of L2 proficiencygroups displayed a significant difference in the frequency of two sorts of lexical errorsincluding spelling and word building only.
(3) Thirdly, three key factors accounted for the phenomenon that a larger numberof morphemes from Chinese were transferred into English written productionsincluding linguistic typology, language proficiency, and recency. Typologically, owingto the same word order of Chinese and English, the lexical transfer of Chinese inEnglish was indispensable, which offered the strongest evidence for its occurrence inL3 English acquisition. Apart from it, with regard to language proficiency, high本论文由英语论文网提供整理,提供论文代写,英语论文代写,代写论文,代写英语论文,代写留学生论文,代写英文论文,留学生论文代写相关核心关键词搜索。

 英国
英国 澳大利亚
澳大利亚 美国
美国 加拿大
加拿大 新西兰
新西兰 新加坡
新加坡 香港
香港 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 法国
法国 德国
德国 爱尔兰
爱尔兰 瑞士
瑞士 荷兰
荷兰 俄罗斯
俄罗斯 西班牙
西班牙 马来西亚
马来西亚 南非
南非






