联系方式
more本类最新英语论文
- 2024-05-03比较文学变异学视角下《酒国..
- 2024-04-25《亨利·沃兹沃斯·朗费罗》..
- 2024-04-15《心灵隐喻:创造性心灵及其..
- 2024-04-05认知语言学视角下《聊斋志异..
- 2024-02-02《世界运行的真正逻辑》(节..
- 2024-01-06文本类型理论下《中国历史精..
- 2023-11-09《蓝袍先生》(节选)汉英翻..
- 2023-08-06《转劣为优》(节选)英汉翻..
- 2023-05-15目的论指导下《瑞肯船东手册..
- 2023-02-02全译论指导下的国际电联期刊..
more热门文章
- 2014-05-26合同的特点及翻译
- 2014-05-27浅议女性用品商标翻译
- 2012-02-10口译文献翻译任务:汉译英精..
- 2014-05-07近代中国俗语的直译与意译-..
- 2014-05-26内地和香港电影片名翻译比较
- 2012-01-12英语翻译论文:南非民主进程..
- 2012-11-10陌生化的角度来看:李清照词..
- 2012-11-12分析总结各类文化负载词的主..
- 2012-11-13体现汉语话语权的翻译方法来..
- 2017-09-05翻译目的论视角下的仓央嘉措..
more留学论文写作指导
- 2024-05-07《湖泊的一生》(节选)英汉..
- 2024-03-31卡森•麦卡勒斯小说中..
- 2024-03-28美国黑人女性心理创伤思考—..
- 2024-03-27乔治·艾略特《织工马南》中..
- 2024-03-21超越凝视:论《看不见的人》..
- 2024-03-19《哈克贝利•费恩历险..
- 2024-03-13心灵救赎之旅——从凯利的三..
- 2024-02-22文学地理学视角下的《印度之..
- 2023-05-03英、汉名词短语之形容词修饰..
- 2023-02-07目的论视域下5g—the futur..
英语名词化的理解和翻译——以《语言的进化》节译为例 [3]
论文作者:留学生论文论文属性:硕士毕业论文 thesis登出时间:2021-09-26编辑:vicky点击率:3737
论文字数:72155论文编号:org202109171151412804语种:英语 English地区:中国价格:$ 66
关键词:英语翻译论文
摘要:本文是一篇英语翻译论文,笔者认为在翻译语言演变的过程中,译者首先对英汉名词化现象有了全面的了解,并在朗格认知理论的指导下,从结构转换和语义转换的角度对这一语言现象进行了研究,通过对从语言演变和相关论文中收集的例子中的名词化现象进行解释,译者采用相应的翻译方法来处理在翻译实践中遇到的问题。
Firstly, in the level of vocabulary, (1) The most common structure is a verbfollowed by ‘- ing’, which is called ‘verb noun’ or ‘action noun’ in syntactic research,while Langacker generalizes it as ‘action nominalization’ or ‘factivenominalization’, read-reading, enjoy-enjoying, consider-considering, etc are all theexamples.
Example 1 Plenty of other modern animals make their living in conditions wherehearing is difficult or impossible.
In this sentence, the word ‘living’ stems from verb ‘live’.
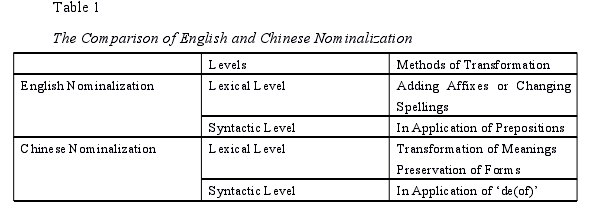
The Comparison of English and Chinese Nominalization
......................
Chapter 3 Translation Methods of Nominalization..........................33
3.1 Translation Methods at the Semantic Level......................................33
3.1.1 Literal Translation............................... 34
3.1.2 Amplification.......................................35
Conclusion...................................... 48
Major Findings......................................... 48
Limitations..............................50
Chapter 3 Translation Methods of Nominalization
3.1 Translation Methods at the Semantic Level
Generally speaking, nominalization is a process of transformation, in which the most obvious character is the change of the structure of language expression, that is,from one form to another. In effect, the change of meaning, which is inescapable, iscaused by the transformation of structure. In other words, the process oftransformation involves not only morphological change, but also meaning change indynamic and static level, and abstract and concrete level. If some texts are translatedwithout considering the logic of nominalization structural transformation andsemantic transformation, the translator will result in mistranslation or omission.According to specific examples encountering in translation practice, the translator hassummarized the following translation methods.
3.1.1 Literal Translation
Literal translation, is once regarded as “rendering, as closely as the associativeand syntactical capacities of another language allow, the exact contextual meaning ofthe original” (p.27), which e本论文由英语论文网提供整理,提供论文代写,英语论文代写,代写论文,代写英语论文,代写留学生论文,代写英文论文,留学生论文代写相关核心关键词搜索。

 英国
英国 澳大利亚
澳大利亚 美国
美国 加拿大
加拿大 新西兰
新西兰 新加坡
新加坡 香港
香港 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 法国
法国 德国
德国 爱尔兰
爱尔兰 瑞士
瑞士 荷兰
荷兰 俄罗斯
俄罗斯 西班牙
西班牙 马来西亚
马来西亚 南非
南非






